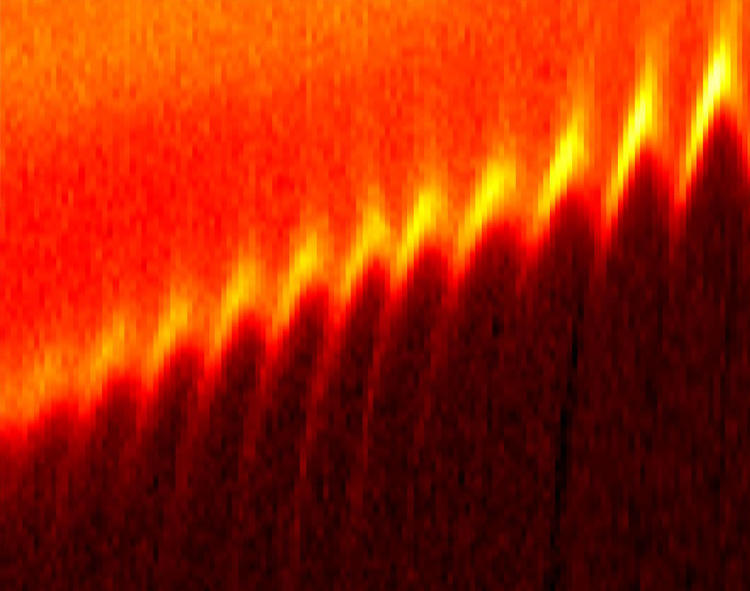
A periodic modulation of critical current.
We have studied edge supercurrents in superconducting topological materials and utilized them to probe interactions between incompatible superconducting condensates in hybrid systems. For the first time, we discovered an intrinsic edge supercurrent in a Weyl semimetal MoTe2. [1] The modulation period of critical current with respect to the applied field corresponds to the physical area of device. This correlation suggests the fluxoid quantization by the edge supercurrent as the origin of the modulation.
When a MoTe2 crystal is coupled to a s-wave superconductor, such as niobium, the incompatibility between the two condensates appears as various experimental anomalies, such as asymmetric noise content in fluxoid-induced oscillations, bimodal stochastic switching of critical current, and anti-hysteretic central peaks. These observations reveal that the unique gap function of device, described by the correlation method of proximity effect, favors the symmetry of the condensate with a larger weighted contribution at a given field. The symmetry that dictates the edge pairing can be inferred from the noise content of edge oscillations, which also uncovers the novel blockade mechanism of s-wave condensate by the intrinsic one. [2]
We are currently conducting experiments that extend from these discoveries, such as tuning the relative strengths of the condensates by additional means. In addition, we are investigating other material platforms that exhibit similar phenomena, such as edge supercurrents and competition between superconducting condensates.
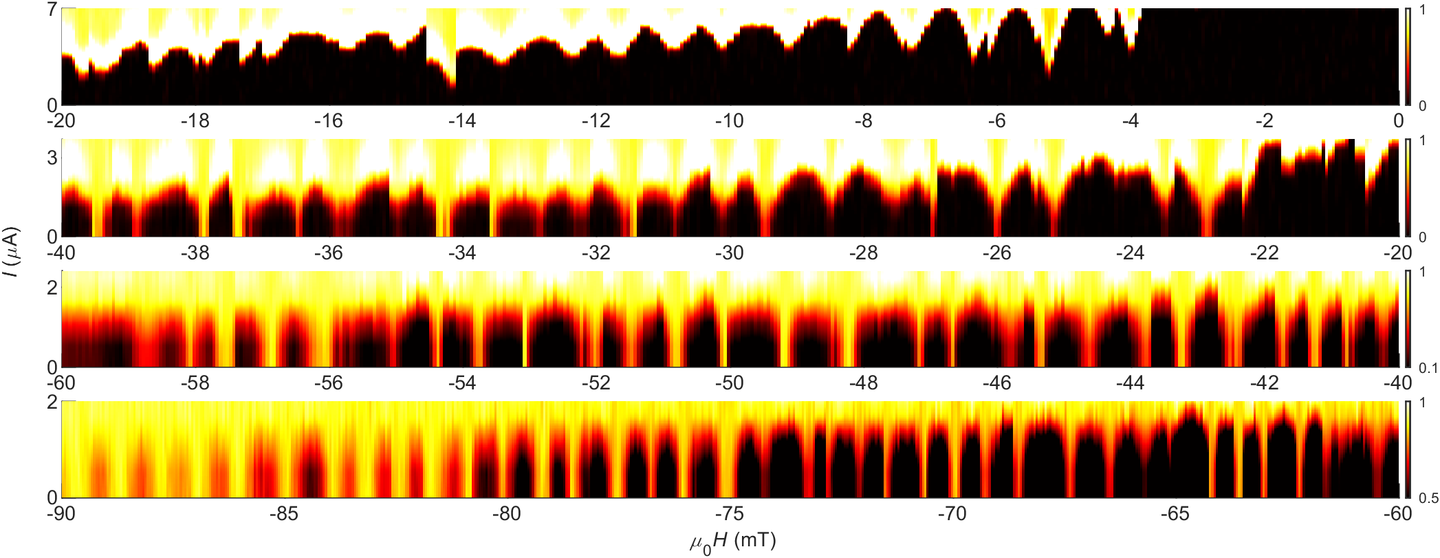
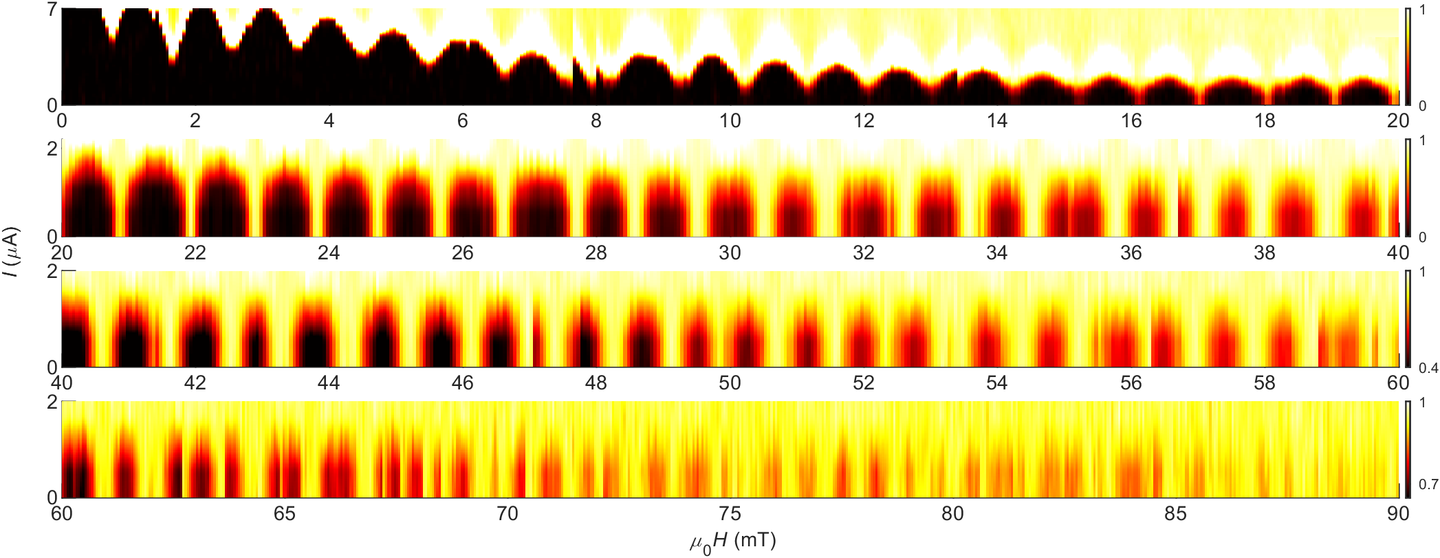
The asymmetric noise content in edge oscillations from a MoTe2 device with niobium electrodes. The profile of inbound (left, dH/dt < 0) oscillations significantly differs from that of outbound one (right, dH/dt > 0).
